Great Himalayan National Park Trek
TREK DIFFICULTY
Moderate
TREK DURATION
3 Days
HIGHEST ALTITUDE
10,170 feet
GROUP SIZE
12
TREK DISTANCE
26 KM
BASECAMP
Himachal Pradesh
BEST TIME
April to June
PICKUP POINT
Himachal Pradesh
Great Himalayan National Park Overview
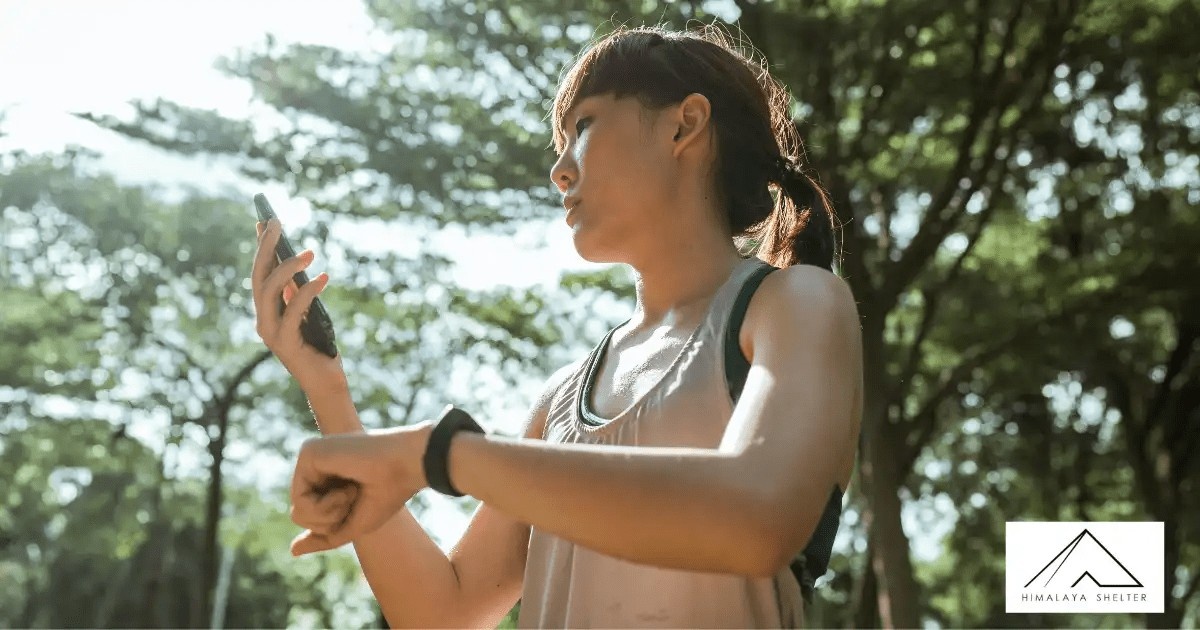
Great Himalayan National Park is one of the most beautiful national parks in our country. GHNP is situated in Kullu, Himachal Pradesh. This national park is situated in the western Himalayas. It is a part of the Himalayan biodiversity hotspot. Great Himalayan National Park is rich in flora and fauna. Its rich cultural heritage makes it unique. This national park was established in 1984. Great Himalayan National Park is globally known for its biodiversity and was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2014. The variations of flora and fauna make this national park a famous spot for trekking.
Trekkers love the Great Himalayan National Park as it offers a wide range of ecosystems. The altitude of this national park ranges from 1500 m to over 6000 m. This makes it adventurous as the trekkers find alpine meadows in lower regions and snowfields in the higher areas. The GHNP has over 375 fauna species and over 1000 fauna species. The national park covers 1171 square km of area which includes big valleys, flights, deep gorges, etc. These beautiful valleys not only look majestic but also provide habitat to various wildlife.
History of Great Himalayan National Park
The concept of establishing a national park emerged in the 1970s when some researchers understood the value of the Himalayan region. They learned about the high-altitude valleys like Nal, Tirthan, and Parvati Valley is home to lots of wild animals and plants. This talk gained potential in the 1980s after lots of conservation moments. It officially became a national park in 1984 with an area of 620 square kilometers.
After becoming a national park, new changes were made like relocating local communities and banning various commercial activities. However, it created conflict between the government and local people. Many livelihoods depended on the forest for grazing cattle, fodder, etc. After making few notations, in the 1990s, people from small hamlets relocated from the designated areas, meanwhile some locals stayed in the buffer zone with limited access. A new project was launched, funded by international agencies to improve eco-tourism. Some alternative livelihood means were introduced like handicrafts and beekeeping.
Today, the Great Himalayan National Park is expanded to 1171 sq km. The human activity inside the national park is very controlled and limited. In 2014, the park became part of the UNESCO World Heritage Site due to its rich flora and fauna.
Highlights of Great Himalayan National Park
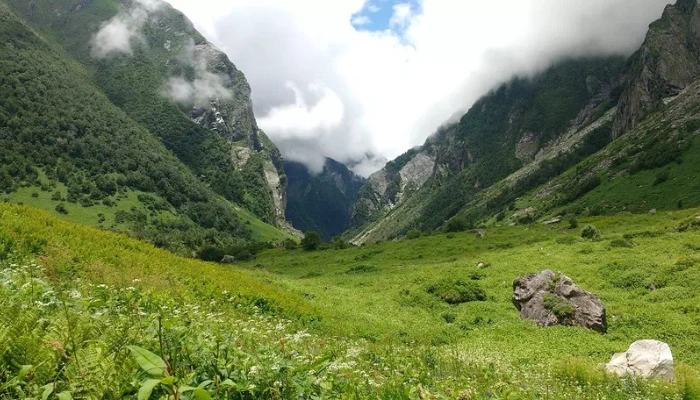
- Beautiful Landscape: The national parks offer a unique biodiversity due to the difference in altitude. The altitude ranges from 1500 m to 6000 m, which means a huge gain in altitude. You can find lush green dense forests, big meadows, and snow-covered peaks. Rivers and waterfalls in valleys aid the beauty of the national park.
- Great biodiversity: The Great Himalayan National Park is home to over a thousand plant species. Many of these plants have good medicinal value. This national park is also native to various wild species. Some of the species are Himalayan Tahr, Musk Deer, Snow Leopard, Himalayan Brown Bear, etc. You can also witness some rare and beautiful birds like the Monal Pheasant, Western Tragopan, etc.
- Heaven for trekkers: This national park is emerging as a great site among trekkers. Trekkers can enjoy the raw and untouched beauty of forests and meadows. There are many campsites near meadows and forests. Some popular treks are Shilt Hut Trek, Tirthan Valley to Rolla, etc. You can trek inside the national park with few regulations.
- Conservation and research: After gaining recognition from UNESCO, Great Himalayan National Park emerged as a great example of sustainable tourism. It is a type of community-based ecotourism. The park management is done by local trained guides. This national park also became a research center for high-altitude flora and fauna, rare species, and climate change.
Difficulty Level of the Great Himalayan National Park
The difficulty level of the GHNP trek depends on trails, altitude, and seasons. Some of the areas below 3000 m are rated easy to moderate. Trekkers can complete these treks without any worry. Meanwhile, some parts of the national park are difficult due to remoteness, high altitude, and rough terrain.
- Easy To Moderate Treks: Treks having an altitude of less than 3000 m such as Rolla Trek, and Shilt Hut Trek are easy. You can find beautiful meadows and dense forests. Trekkers do not gain lots of altitude so it makes the trek beginner-friendly. Various campsites are available so the trekkers can plan 2-3 days in the national park.
- Moderate To Difficult Treks: The trek's difficulty depends on the altitude. Treks such as Jiwa Nal Valley Trek, Tirthan Valley to Rakhundi Top Trek are rated as moderate to difficult. Trekkers have to walk long distances and have very steep climbs. Some of these treks also have river crossings that aid the difficulty level.
- Difficult Treks: All the treks above 4000 m are rated as difficult. Some of the difficult treks are Raktisar Trek, Jiwa Nal to Parvati Valley Crossover, etc. These treks take 6-10 days and require long-walking hours daily. High altitude can also cause AMS. These treks are only advisable to people who are experienced in high-altitude trekking.
Best Time To Visit Great Himalayan National Park
You can plan your visit to Great Himalayan National Park around the year. The national park always offers a beautiful landscape to the visitors. Meanwhile, the experience in every season will be different.
- Great Himalayan National Park from April to June
This is the best time to plan your trip. The weather is beautiful and cool. The snow starts melting in the higher areas and most trekking trails start opening. You can also witness rhododendrons and wildflower blooming.
- Great Himalayan National Park from July to Mid-September
This is the monsoon season and most of the treks can be risky. You can plan low-altitude treks as the trails will be quiet and less crowded. People who love trekking in lush green areas can plan the trip. But trekking at high altitude can be very risky.
- Great Himalayan National Park from Mid-September to Mid-November
Post-monsoon, the weather becomes pleasant with clear mountain views. This is the best time for trekking. The air will be crisp and you can see beautiful snow-capped peaks. The trails will be dry and the landscape will start turning golden.
- Great Himalayan National Park from Late November to March
This season is good for snow lovers. Trekking at high altitudes is difficult with limited reachability. The trekkers will require special snow gear and guidance. However, the lower-altitude regions offer an excellent space for witnessing a magical winter.
How to Reach the Great Himalayan National Park?
You have to reach Aut to trek the Great Himalayan National Park. Most people start the trek from Gushaini which is the main and most popular entry point. You can also enter the national park via Sainj Valley which is quieter but has a very remote point.
- Route 1: Delhi to Aut
Delhi is connected to almost all the big cities of our country. You can take a flight or train to Delhi. After reaching Delhi, take a bus to Aut. Both HRTC and private bus services are available.
- Route 2: Chandigarh to Aut
Chandigarh is also a well-connected city and you can find trains and flights from various locations. You can take a train to Chandigarh and then complete the journey via bus. HRTC buses and other private services are available from Chandigarh to Aut.
You can also take a flight to Bhuntar Airport. You can find regular flights from Delhi and occasional flights from Chandigarh. Various local bus and private taxi services are available from Bhuntar Airport to Aut. The nearest railway station is Joginder Nagar Railway Station (110 km from Aut). However, the railway connectivity to this station is limited.
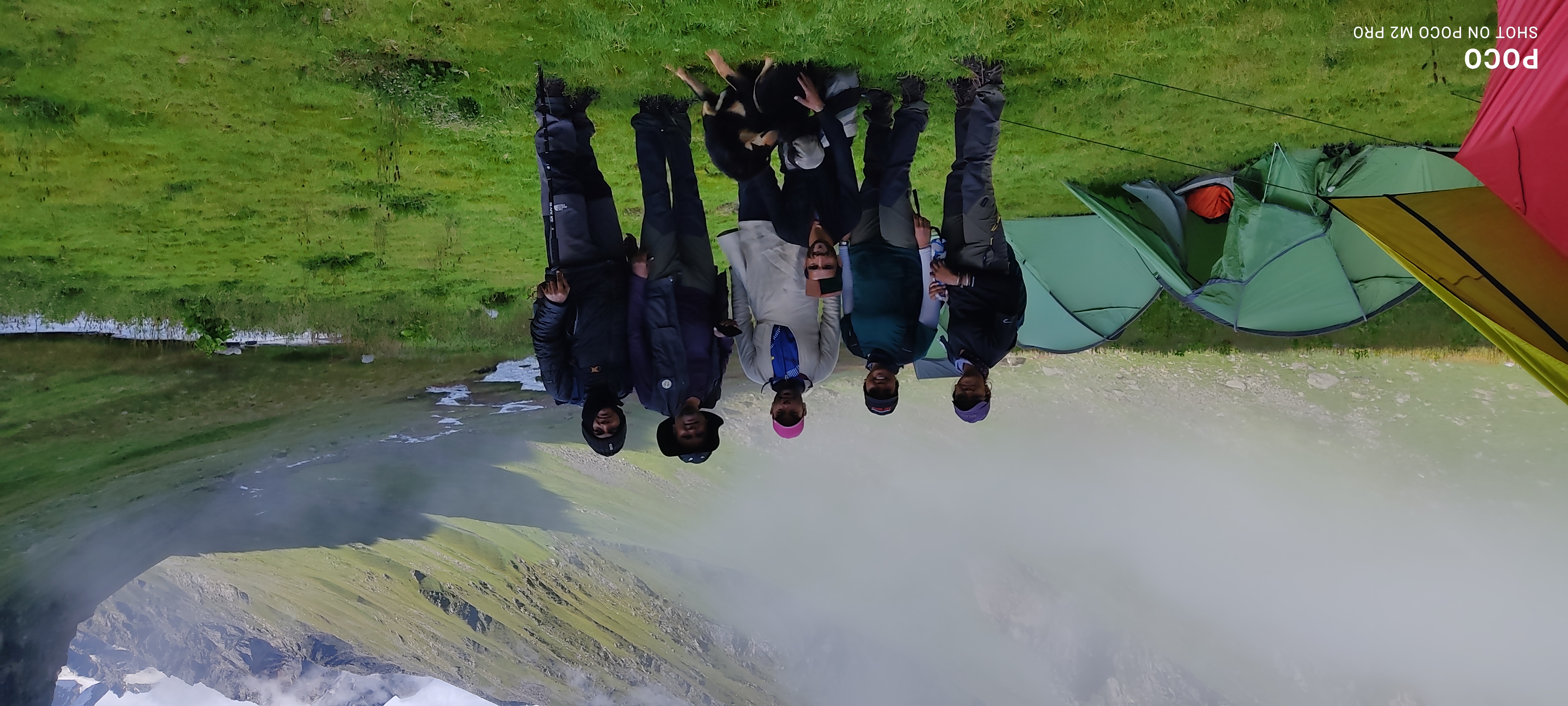
Day 1: Reach Aut early morning and have breakfast. Start your trek from Aut to Rola via Goshaini. The trek distance is 9 km and will take 5-6 hours.
Day 2: Start your trek from Rola to Shilt. After a short halt, trek back from Shilt to Rola. The trek distance is 8 km and will take about 4 hours.
Day 3: Start your trek from Rola to Aut. The trek distance is 9 km and will take about 4-5 hours. You can stay at Aut and enjoy the locality or you can take a bus back to your city.
The GHNP is one of the most beautiful Himalayan national parks. Plan your tailored Great Himalayan National Park trek with us. The Himalayan Shelter team offers a customized and well-planned trek to you. We believe in humble group size and maximal experience. You can plan your trip with your friends and family to enjoy the trek at its best.
The Himalayan Shelter trek is for people who are craving adventure and zeal. Our team ensures safety and eco-friendly practices. We provide customized stay, meals, and activities. The guides are certified and have good experience in high-altitude trekking. Our team will design the trek as per your interests, pace, and fitness level. We believe in an authentic experience and try our best to keep everything local and beautiful. With the Himalayan Shelter team, you will enjoy the beauty and thrill of mountains.
Day 1: Aut to Rola via Goshaini
Trek: 9 km, 5 to 6 hours
Altitude Change: 1,000 m to 2,100 m
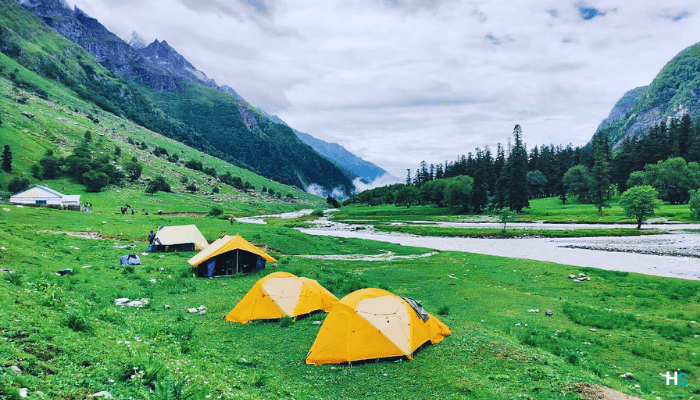
Stay: Camping (Alpine tents)
Meals: BLSD (Breakfast + Lunch + Evening Snacks + Dinner)
Start early from Aut. You will drive about one hour to Goshaini. This is where the trek begins.
You walk next to the Tirthan River. The path goes through forests. You will see deodar, pine, and rhododendron trees. It is an easy, gentle climb. You will pass small wooden houses. You will also see open fields. Listen for the birds and the running streams.
The walk is steady. You will stop a few times for snacks and to take pictures. You arrive at Rola. This is a quiet campsite by the river. You will have tea and a simple dinner. Tents will be set up. Just relax in the mountain air.
Day 2: Rola to Shilt; and back to Rola
Trek: 8 km total, 4 hours
Altitude Change: 2,100 m to 2,500 m
Stay: Camping (Alpine tents)
Meals: BLSD (Breakfast + Lunch + Evening Snacks + Dinner)
Walk after breakfast. You go through thick forest and open spots. The climb to Shilt is steady, but not too hard. You will have plenty of shade. This is a good chance to see Himalayan birds. Shilt is a meadow with great views of the snow peaks. You will rest and eat lunch outside. After a short break, you walk back down to Rola. The afternoon is free. You can take short walks, sit by the river, or watch birds. Have a warm meal as it gets dark in the valley.
Day 3: Rola to Aut | Trek: 9 km in 4 - 5 hrs
Trek: 9 km, 4 to 5 hours
Altitude Change: 2,100 m to 1,000 m
Stay: None (end of trek)
Meals: BL (Breakfast + Lunch)
Start early. You walk the same path back from Rola to Goshaini. You pass familiar forests and river spots. It is a gentle but steady downhill walk. Sunlight comes through the tall trees. You reach Goshaini by noon. Then you drive to Aut for your next trip. The trek is over. You leave with memories of quiet paths and scenic valleys. You can have a late lunch at a local café before you leave if you want.
Our treks are specially designed by the experienced team at Himalaya Shelter taking you on an adventure of a lifetime all while making you connect not only with the bountiful nature but also with yourself and with others on the trek with you creating wonderful memories which will last you a lifetime. All Himalaya Shelter treks are guided by experienced Trekkers having vast knowledge and experience of the region, providing with insightful information and stories pertaining to the region’s flora and fauna and the history of the region whilst the trek. It is safe to say that on successfully completing the trek one will gain tremendous insight and experience along with lifetime memories.
Trek Inclusions
- TRANSPORTATION - Support from Aut
- Accommodation – At Base Camp, stay at a local homestay or guest house for one night each, which will give you an insight into the authentic lifestyle of the locals.( INR 5000 per person extra for single sharing throughout the trek )
On Trek stay in a 2-person Vango Halo Pro/A-Shape tent, which is to be shared by two trekkers, built to withstand extreme weather conditions and at the same time making you comfortable after a hard day’s trek. - Camping Equipment – specially designed sleeping bags that can withstand harsh weather conditions, foam mattresses. Other safety gear like microspikes, gaiters, an ice axe, and helmets will be provided.
- Medical Kit – our team will be equipped with an extensive medical kit, which our team is trained and experienced to use. Oxygen cylinders are used after they are thoroughly inspected throughout the Trek. Even campsites have large oxygen cylinders as backups.
- Permission - Forest entry charges for Indian nationals (Additional charges will be applicable for international tourists)
- Meals – Breakfast, packed lunch (on trek days), evening snacks, and dinner will be served. A hearty, delicious, and nutrition-filled Veg meals with egg preparation will be provided throughout the trek. (Jain and Vegan Food can also be arranged on prior notification.)There will be a dedicated Kitchen Tent along with a dining tent, which will have a dining table too.
- Our Team – A highly experienced and AMC-certified Trek Leader who will help ensure that the entire trek goes smoothly and safely while navigating the challenging conditions during the trek, and is skilled enough to navigate any medical emergency that can arise during the trek. Local and route Guides who are well-versed with the region and provide an in-depth insight into the local customs and knowledge of the flora and fauna endemic to the region. A dedicated Kitchen staff, which includes a Cook, a helper, and other support staff. There will also be porters and mules to carry common equipment.
- Cloakroom - We have a cloakroom facility available for extra luggage. Every trekker is permitted to leave their luggage behind at no charge.
Trek Exclusions
- Personal expenses like tips, personal medicines, phone calls etc.
- Travel Expenses - Travel expenses from your hometown to the mentioned Pick-Up Point are not included in the trek fee.
From the scheduled pick-up spot to the base camp, we have our own fleet of vehicles like Bolero, Innova, Dezire, or Tempo Traveler (12-seater). This is be shared by trekkers for a pre-decided amount. All vehicles are non-AC. - Personal Equipment - Any personal gear like jackets, shoes, cutlery, or backpacks are not included in the trek fee. We recommend renting them from our Rental Store for an affordable fee. This can be pre-arranged to avoid last-minute hang-ups.
- Offloading - We encourage carrying your backpack to get into the true spirit of trekking. However, if needed, you can opt to offload your personal luggage of up to 12 kgs for an additional cost of INR 500 per bag per day.
- Trek Insurance - A mandatory trek insurance fee is charged in addition to your trek fee. Since most medical insurance doesn’t cover adventure activities, trek insurance offers essential coverage, enhancing your safety without a significant financial burden.
- Buffer day on the trek - We have kept a buffer day on the trek to account for any weather-related delay. If this is utilized, you will need to pay an extra amount to your trek leader.
- Anything apart from inclusions
- Please carry a lunch box for a packed lunch/breakfast to avoid using polythene and Aluminium foil.
Keeping the Himalayas clean is our own responsibility. Reduce the use of Plastic when you are in the abode of the Sacred Himalaya. 🌱
You can plan your trip from April to June or September to November for the best experience.
Yes. You need an entry permit from the GHNP office. For trekking, you need to hire a registered guide.
Yes. You can do low-altitude treks like Rolla Trek or Shilt Hut Trek as a beginner.
Yes. The national park opens in the winter but with limited access.
Read More on Great Himalayan National Park Trek
Treks by Categories
Treks By Month
Treks By Experience